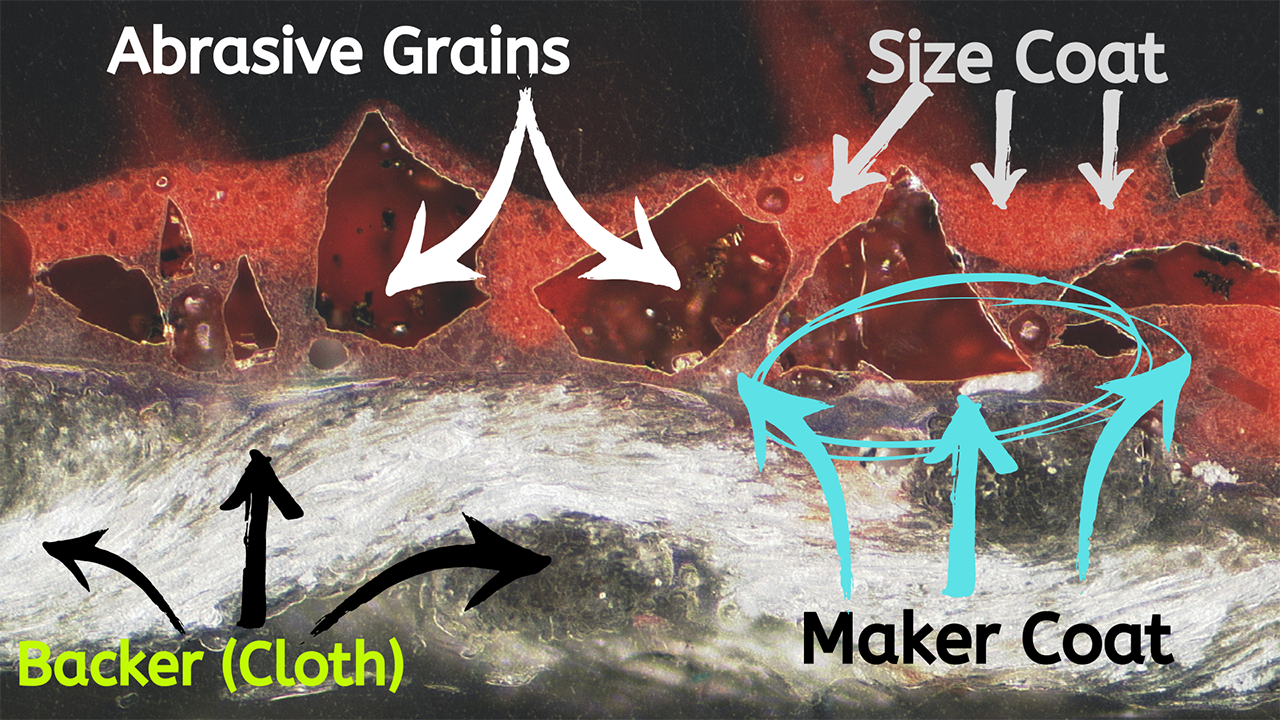
When it comes to selecting the right coated abrasive for your specific application, the process can be overwhelming given the variety of materials, grit sizes, and backing options available. As a manufacturer of silicon carbide and aluminum oxide abrasives, we understand the importance of choosing the correct abrasive to achieve optimal results. In this blog post, we will guide you through the key factors to consider when selecting a coated abrasive, ensuring that you make an informed decision for your projects.
1. Understand the Material Type
The first step in selecting a coated abrasive is to understand the material you will be working with. Different materials require different abrasives for effective processing:
- Silicon Carbide: Known for its hardness and sharp cutting ability, silicon carbide is ideal for cutting and grinding harder materials such as ceramics, glass, stone, and non-ferrous metals. It provides a consistent finish and is perfect for applications requiring a high level of precision.
- Aluminum Oxide: This abrasive is more versatile and is commonly used for wood, metal, and plastic. Aluminum oxide is durable and tough, making it suitable for grinding, sanding, and polishing. It’s also an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications where longevity is critical.
2. Consider the Grit Size
Grit size is another crucial factor in abrasive selection. The grit size determines the coarseness of the abrasive:
- Coarse Grits (24-60): These are best for aggressive material removal, shaping, and preparing surfaces. Coarse grits are ideal for heavy sanding tasks or when a rough finish is acceptable.
- Medium Grits (80-120): Suitable for intermediate sanding and smoothing surfaces. They provide a balance between material removal and finish quality.
- Fine Grits (150-240): Used for finishing touches and smoothing out surfaces to prepare for painting or coating. Fine grits are also ideal for achieving a polished look on metals or plastics.
- Very Fine Grits (320 and above): Best for polishing and achieving a mirror-like finish. These grits are used for the final stages of finishing, particularly on metals and other hard materials.
3. Evaluate the Backing Material
The backing material of the abrasive plays a significant role in its performance and durability. Common backing materials include:
- Paper: Light and flexible, paper-backed abrasives are typically used for hand sanding or in situations where flexibility is needed. They are less durable than other options and are best suited for light-duty applications.
- Cloth: Cloth-backed abrasives are more durable and tear-resistant, making them suitable for machine sanding and heavy-duty applications. The flexibility of cloth allows for more aggressive material removal and is often used in belt sanders.
- Fiber: Fiber-backed abrasives are stiff and provide excellent support for heavy grinding and finishing tasks. They are commonly used with disc sanders and offer a longer lifespan compared to paper or cloth backings.
4. Match the Abrasive to the Application
It’s essential to match the abrasive type to the specific application to achieve the best results. Consider the following applications:
- Cutting and Grinding: For these tasks, silicon carbide abrasives are typically preferred due to their sharpness and hardness. They can cut through hard materials efficiently and are often used in precision grinding.
- Sanding and Polishing: Aluminum oxide abrasives are ideal for sanding and polishing tasks, particularly on softer materials like wood and plastic. Their durability ensures a long lifespan even under heavy use.
- Surface Preparation: If your project involves preparing surfaces for painting or coating, selecting the right grit size is crucial. Medium to fine grits are typically used to smooth the surface and remove imperfections.
5. Consider the Environment
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can impact the performance of your coated abrasive. Silicon carbide is more resistant to high temperatures, making it suitable for high-heat applications. Aluminum oxide, on the other hand, is more resistant to chemical wear and can be used in various environments.
6. Test and Evaluate
Finally, it’s always a good idea to test different abrasives before committing to a large order. Testing allows you to evaluate the performance of the abrasive on your specific material and ensure it meets your quality standards. Keep in mind that different batches may have slight variations, so it’s essential to evaluate each batch.
Conclusion
Choosing the right coated abrasive is critical to the success of your project. By considering the material type, grit size, backing material, application, and environmental factors, you can make an informed decision that will enhance your efficiency and the quality of your work. Whether you’re working with silicon carbide or aluminum oxide abrasives, understanding these factors will help you achieve the best results every time.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that you select the most suitable abrasive for your needs, leading to improved productivity and a superior finish. For more information on our range of silicon carbide and aluminum oxide abrasives, feel free to contact us. We’re here to help you make the right choice.